Since the first version of the Hyper-V server, back in 2008, until now, the networking within the product has remained consistent. It operates in the same way. There are three available virtual switches: private, internal, and external. Each of these switches provides a different type of connectivity. The same concept applies to any version of the Hyper-V server, including the Hyper-V client on Windows 8 and later versions.
Table of Contents
- Private network switch
- Internal network switch
- External network switch
- How to create a virtual switch
- How to assign VM with a virtual switch
- Wrap up
This article aims to provide guidance on the differences between private, internal, and external virtual network switches and assist you in choosing the one that best suits your needs.
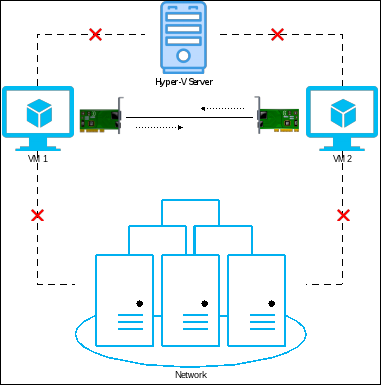
Private network switch
The private switch allows communication only between virtual machines hosted on the Hyper-V host. All VMs must be assigned to the private switch to communicate with each other. You will need to manually define IP addresses on the VMs unless one of the VMs is acting as a DHCP server. The VMs cannot communicate with the host or the rest of the network.
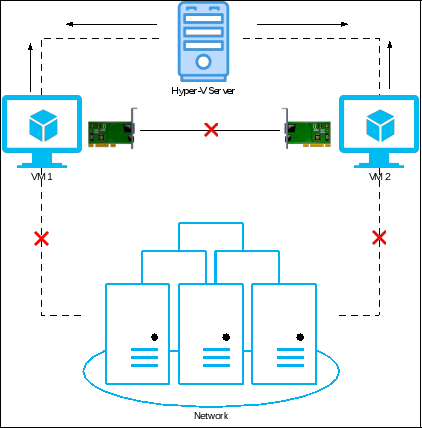
Internal network switch
The internal switch allows communication between virtual machines and the Hyper-V host. Once you create an internal switch, Hyper-V will create a new network card on your Hyper-V server where you will need to enter an IP address. You will also need to do the same on the VM so that both the VM and Hyper-V are in the same network and subnet. Your VM cannot communicate with other VMs or the rest of the network.
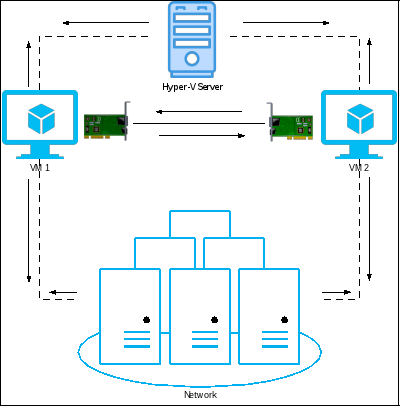
External network switch
The external switch allows your VM to communicate with other VMs assigned to the external switch, your Hyper-V host, and the rest of the network. If you already have DHCP in your LAN, it will assign a new IP to your VM since it resides on the same network.
Can a VM be connected to multiple network switches in Hyper-V? Yes, it can. A single VM can be assigned to private, internal, and external at the same time.
How to create a virtual switch
You can create network switches using either the GUI through Hyper-V Manager or by utilizing PowerShell. In this case, we will be using Hyper-V Manager.
- Open Hyper-V Manager.
- On the right side, click on Virtual Switch Manager… under the “Actions” section.

Hyper-V Manager | Virtual Switch Manager - On the left side of the device tree, select New virtual network switch.
- Choose the virtual network switch you want to create and click on Create Virtual Switch

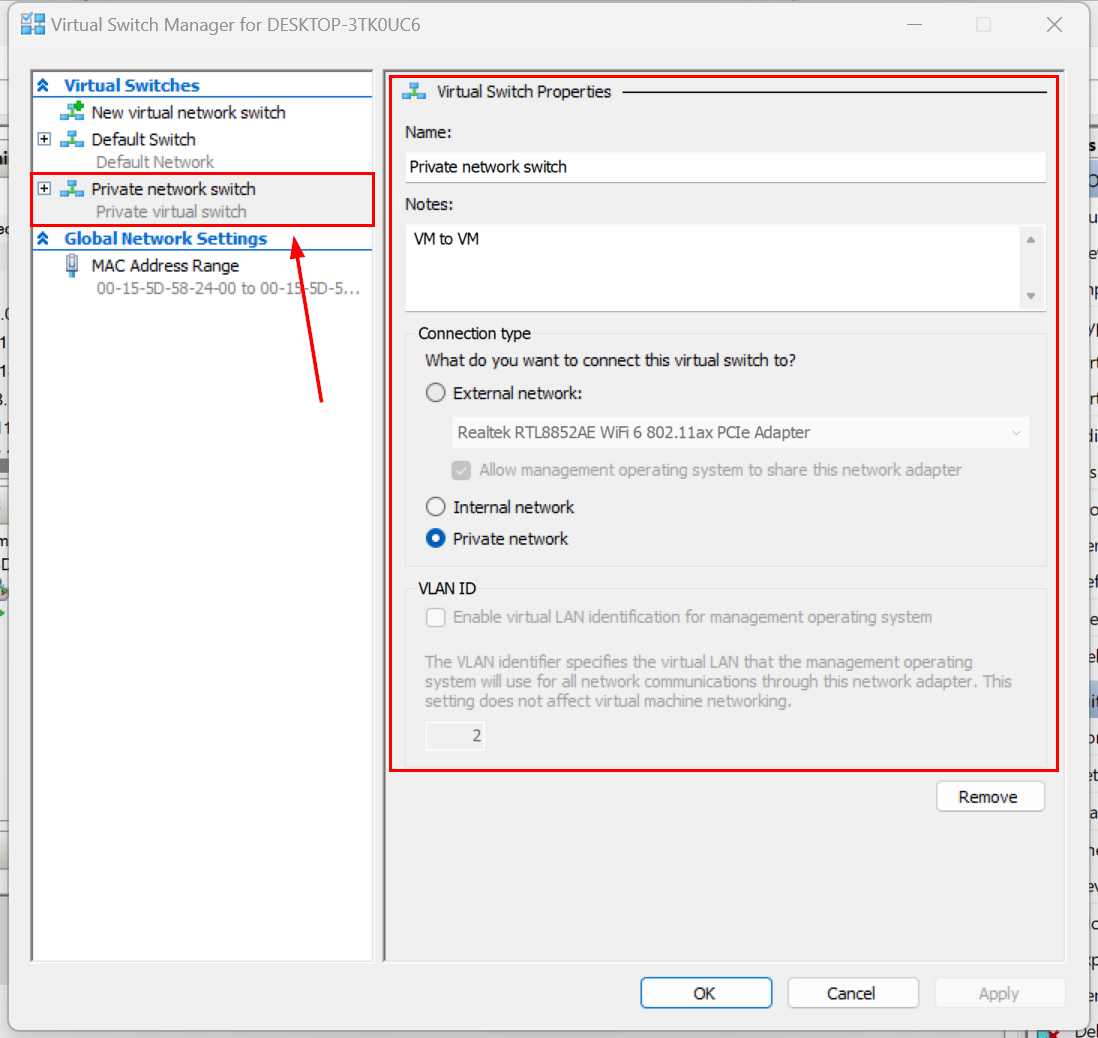
Select the virtual switch If you select Private, enter the name of the virtual switch, and then click on Apply and OK. You can also optionally add notes if desired.

Configure private network switch If you select Internal, enter the name of the virtual switch, and then click on Apply and OK. You can also optionally add notes if desired.
You can also enable virtual LAN identification for the management operating system under VLAN ID. What does this mean? In a scenario where you have multiple virtual machines (VMs) hosted on a Hyper-V server, you may want to separate the management operating system from the VMs by creating an internal network switch. By assigning a specific VLAN ID to the internal network switch, you can logically isolate the management operating system’s network traffic from the VMs.

Configure the internal network switch If you select External, you should also add the name of the virtual network switch, choose the physical network adapter, and then click on Apply and OK. Additionally, you have the option to select Allow management operating system to share this network adapter.
As mentioned previously for the internal switch, you can also enable virtual LAN identification for the management operating system under a VLAN ID for the external switch. This feature allows you to logically separate the network traffic of the management operating system from that of the virtual machines (VMs) hosted on a Hyper-V server.

Configure the external network switch - Once you create a new virtual switch, it will be added under the Virtual Network Switch tree. If necessary, you can modify the settings of the virtual switch.
How to assign VM with a virtual switch
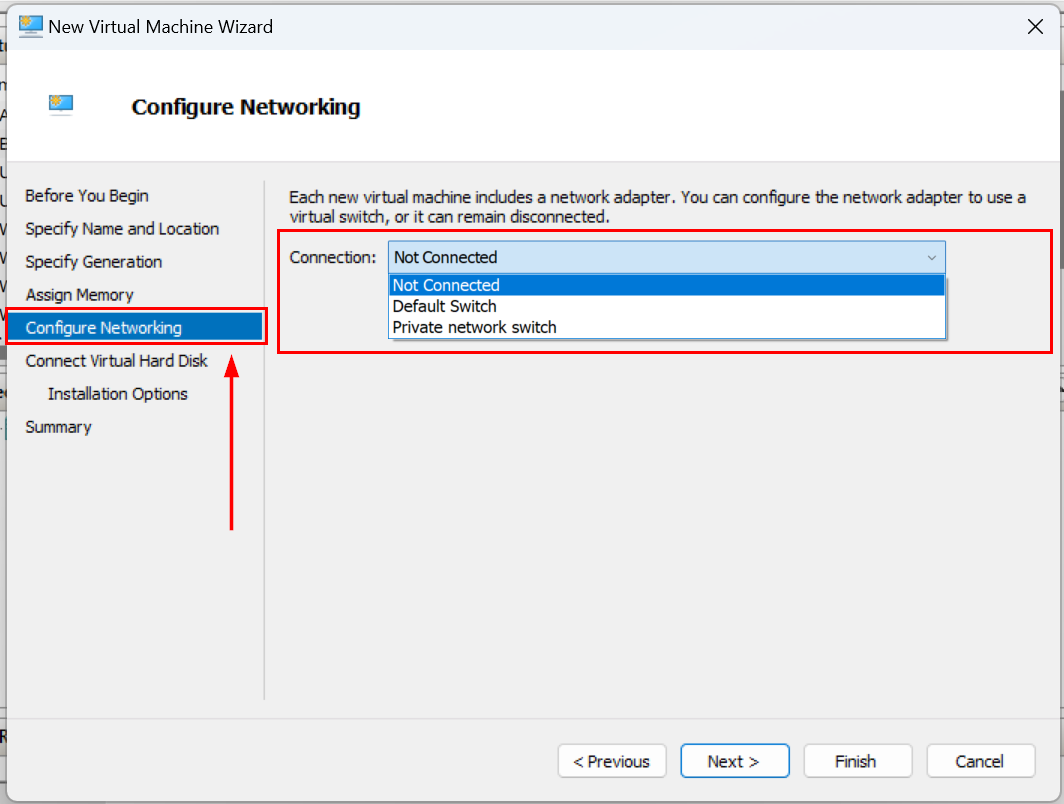
Once you create a virtual network switch, you can proceed to assign it to either a new or an existing virtual machine. If you are creating a new virtual machine and reach the Configure Networking section, you will need to choose the created virtual network switch under the Connection option. Then, you can continue with the creation of the new virtual machine.
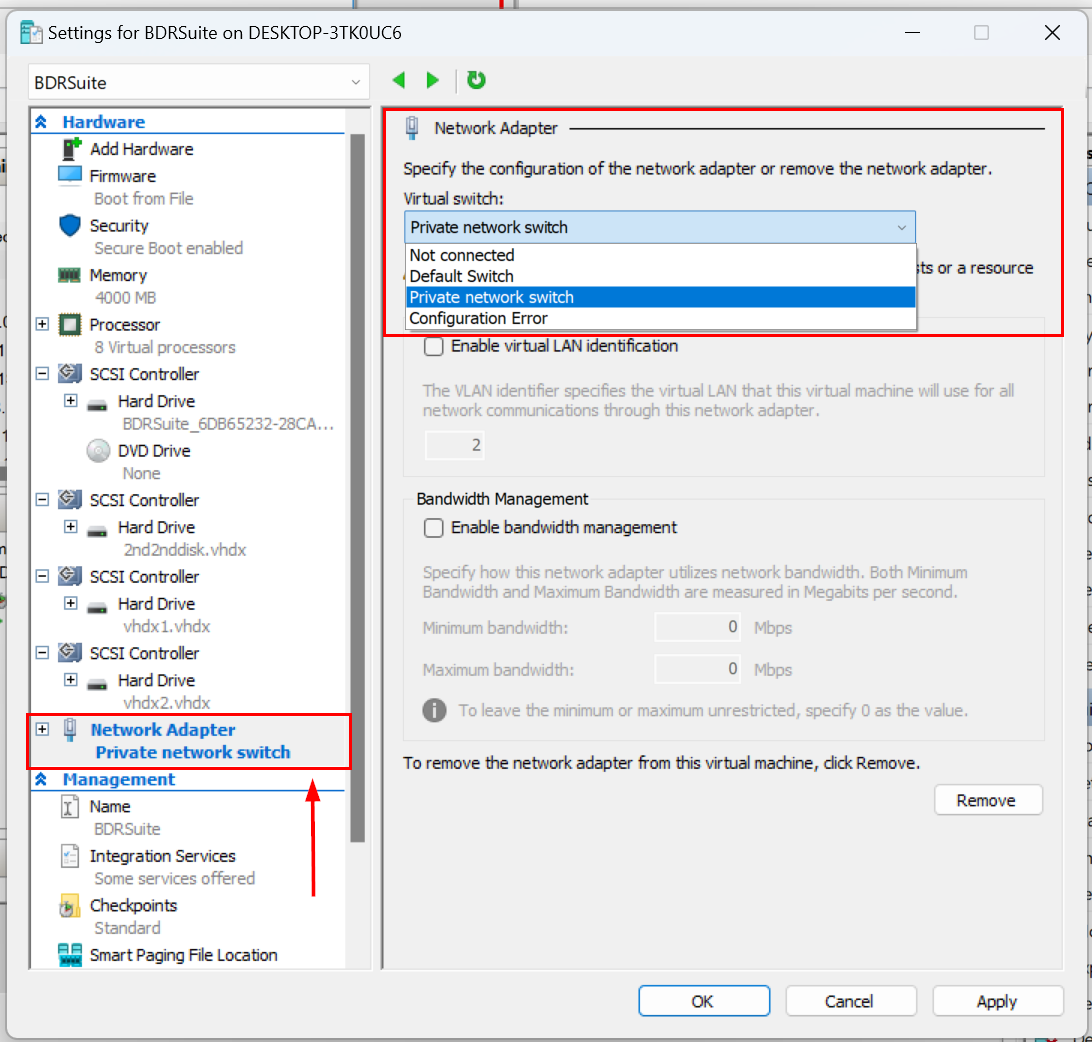
If you want to modify the network settings of an already created virtual machine, you can do so by following these steps:
- Right-click on the virtual machine and select Settings
- In the settings window, navigate to Network adapter on the left side under the Hardware section
- From there, you can change the virtual switch by selecting a different option under the Virtual switch setting
You can do it while your VM is running.
Wrap up
Hyper-V provides three virtual network switches: private, internal, and external. The private switch enables communication between VMs, the internal switch allows communication between VMs and the host, and the external switch enables communication with the network. You can create virtual network switches using both Hyper-V and PowerShell. Once created, you can assign them to new or existing virtual machines.
This article covers the details to help you understand the differences and guides for creating and assigning virtual network switches to VMs.
Easily elevate the security of your Hyper-V setup by obtaining BDRSuite: Download BDRSuite
Uncover the full scope of Hyper-V backup potential with BDRSuite and observe its effectiveness firsthand: Hyper-V Backup with BDRSuite
Related Posts:
Hyper-V Networking Configuration Best Practices
Hyper-V Virtual Switch – Part 3 – Managing Hyper-V virtual switches
Best Practices for Hyper-V storage and Network configuration
Virtualization Trends Series: Network Virtualization: Transforming the World of Networking : Part 7
Hyper-V Virtual Switch – Part 2 – Creating Hyper-V Virtual Switches
Connecting Hyper-V Virtual Machines to the Physical Network
Hyper-V Network Virtualization Overview and Tools
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.

